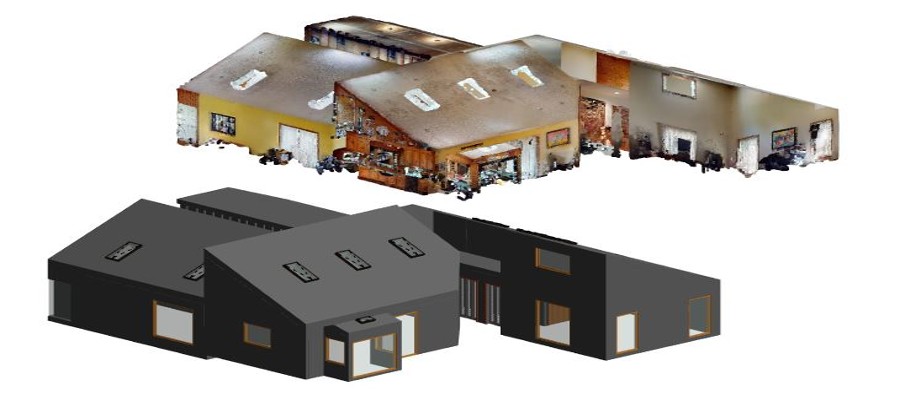
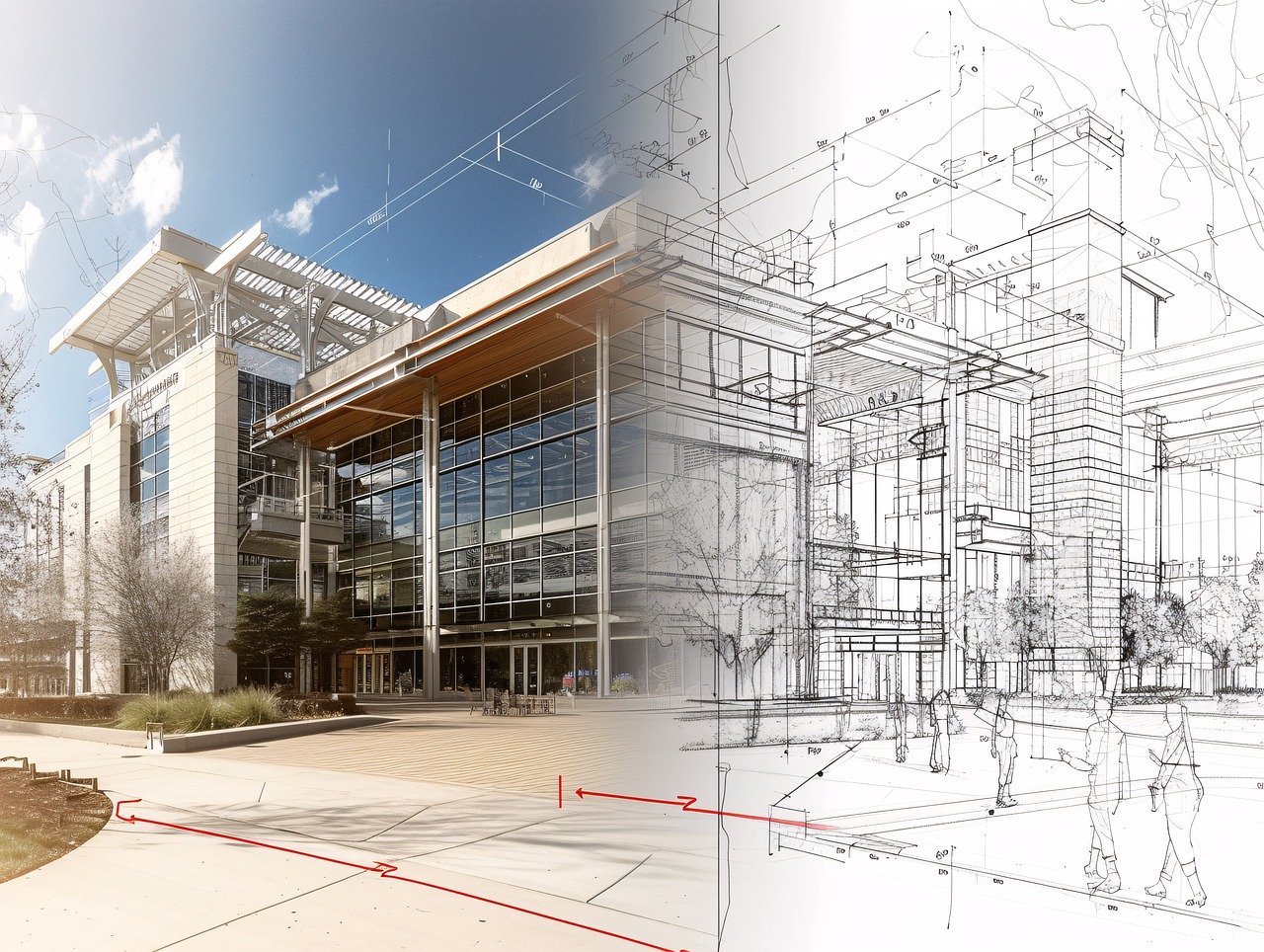
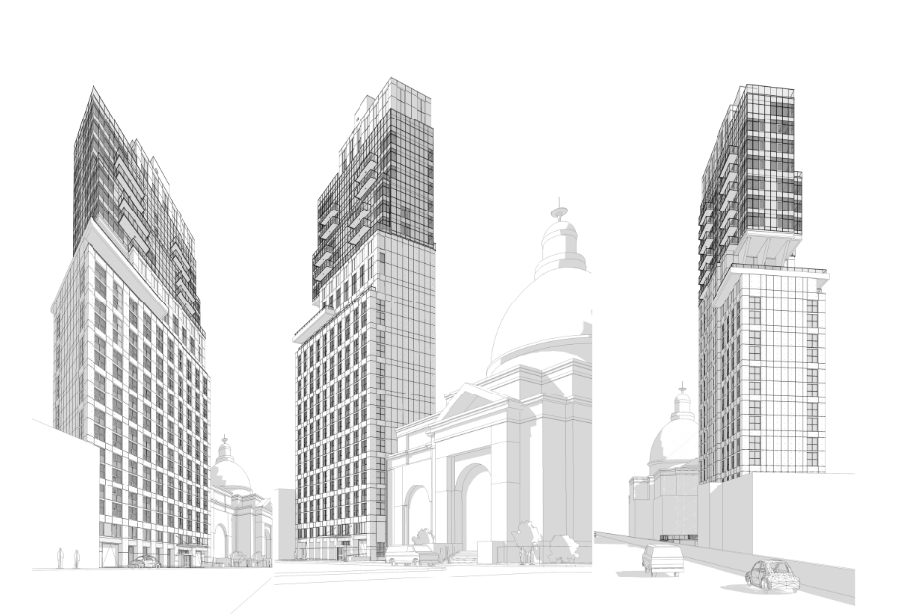
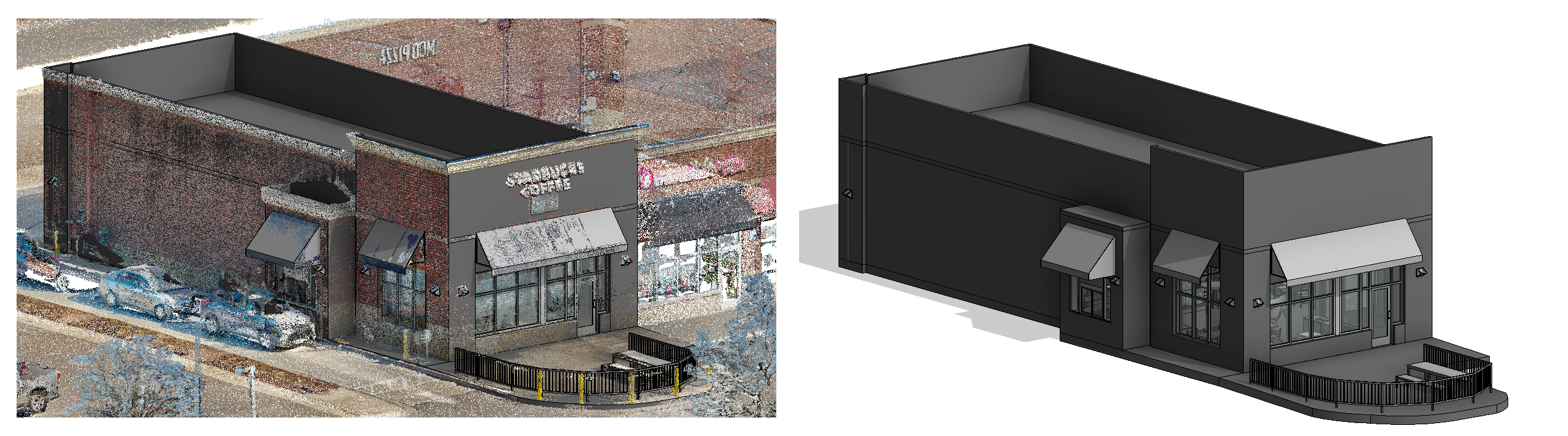
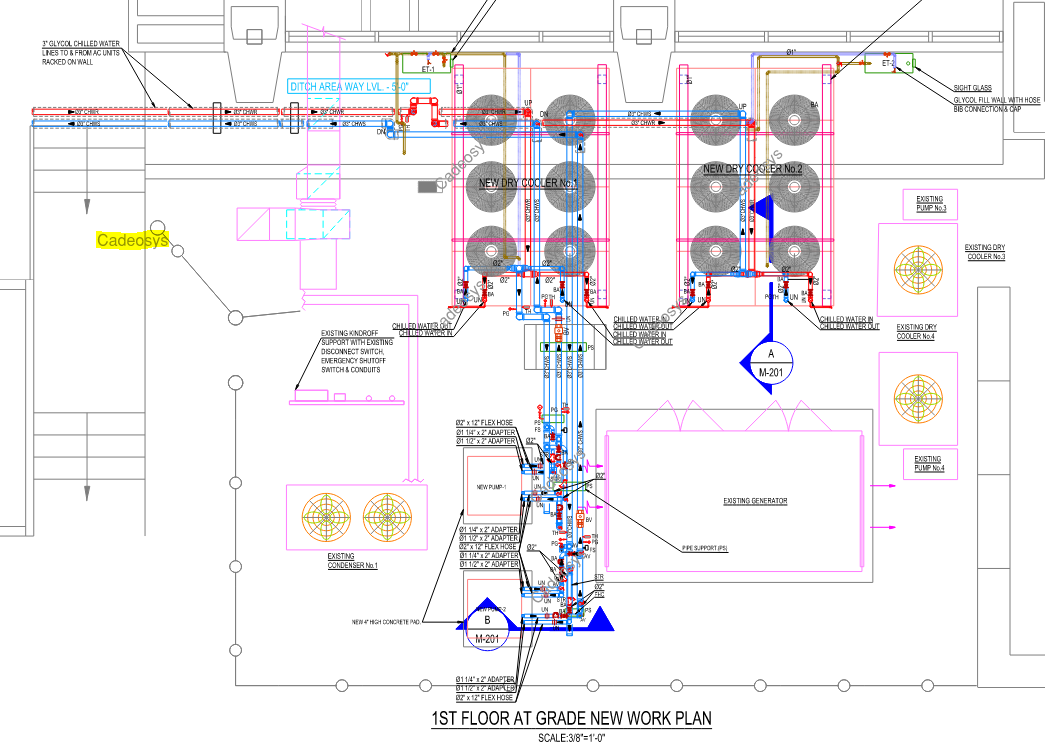
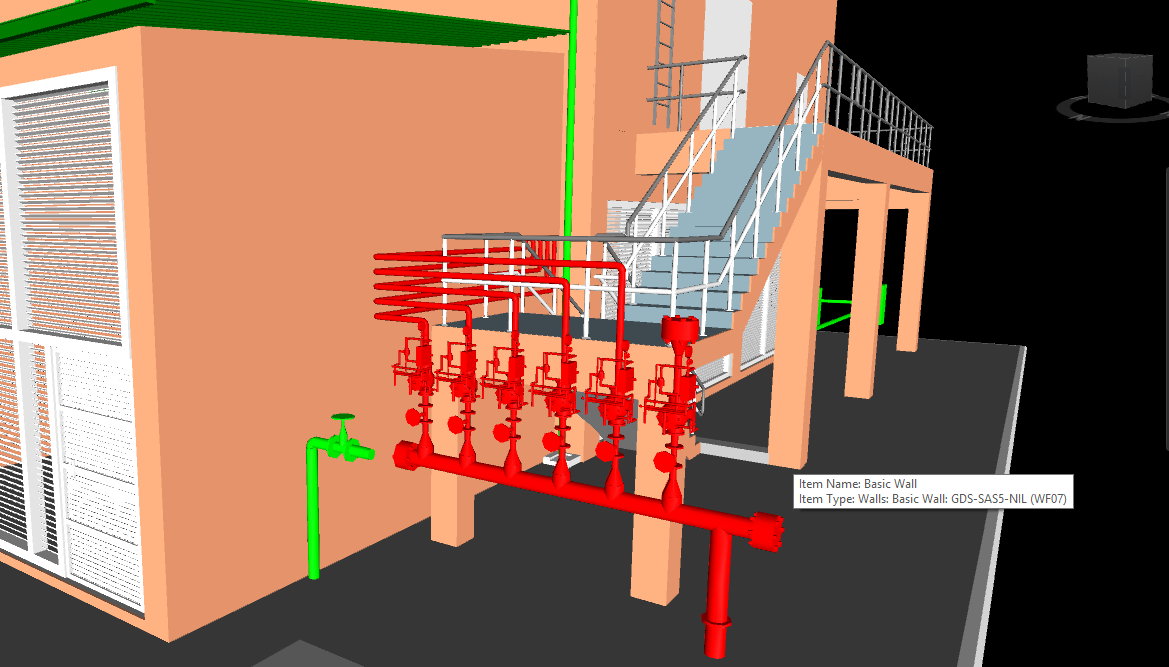
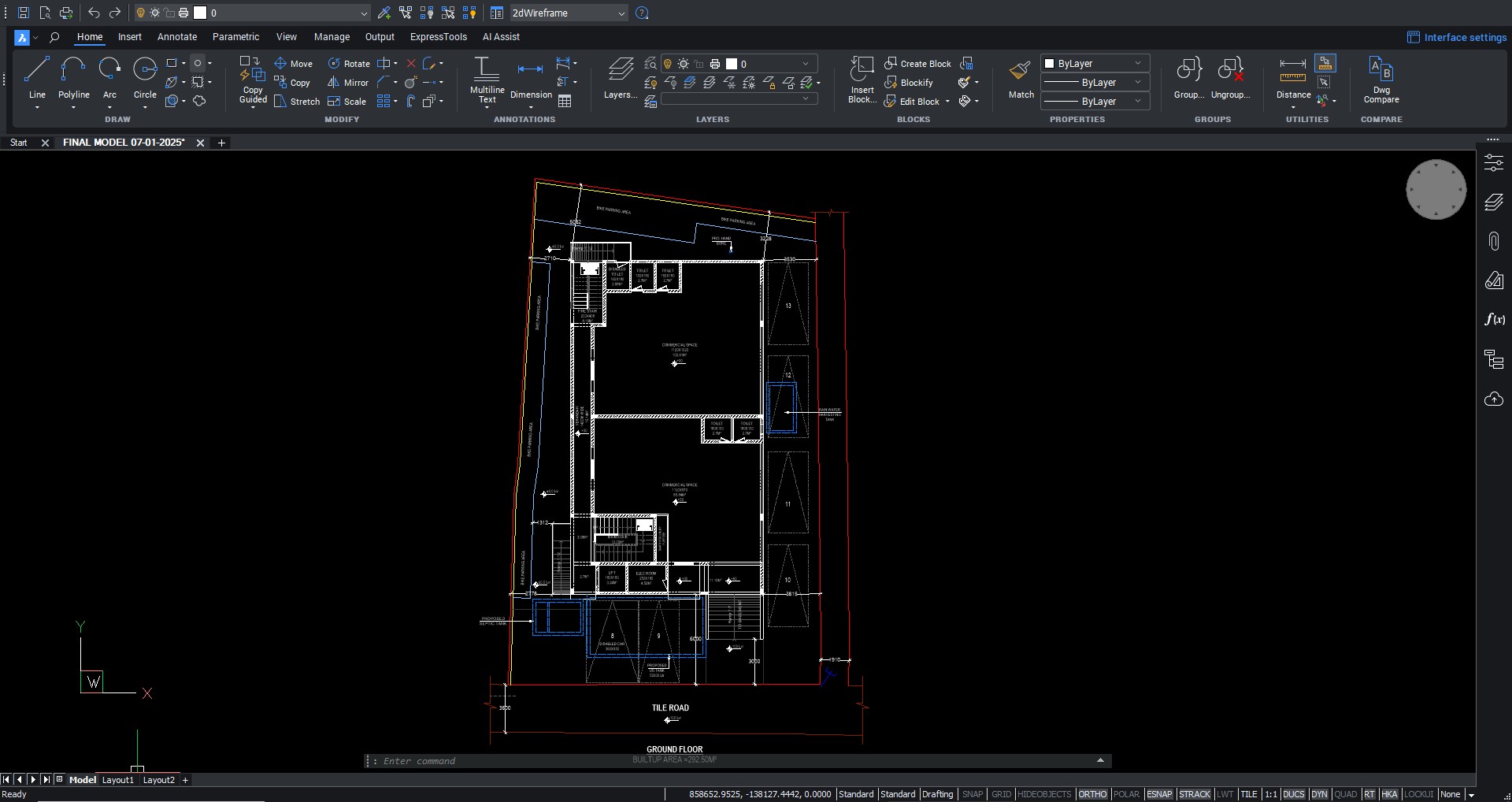
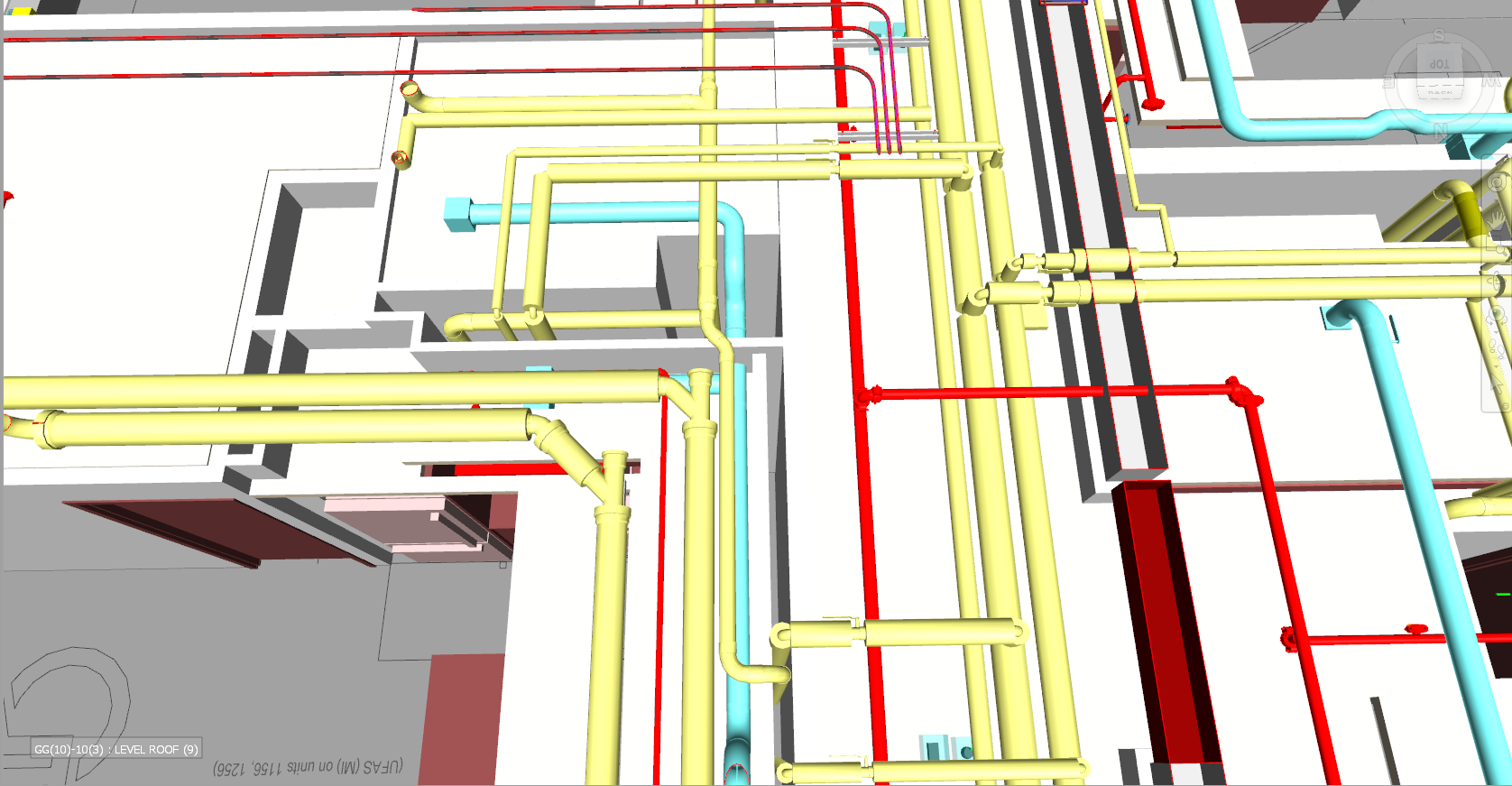
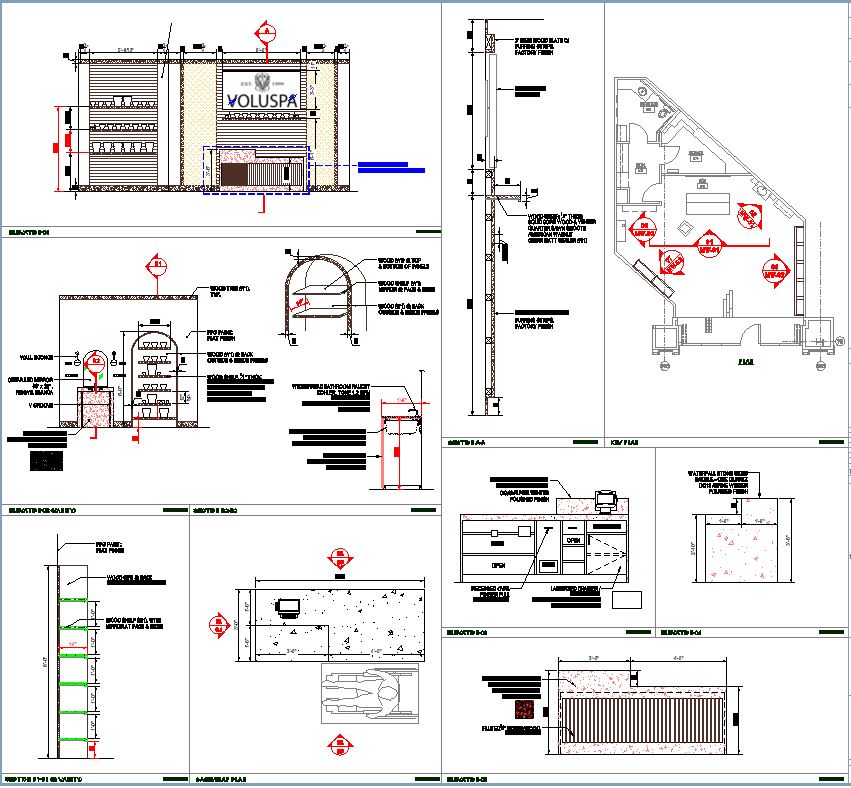
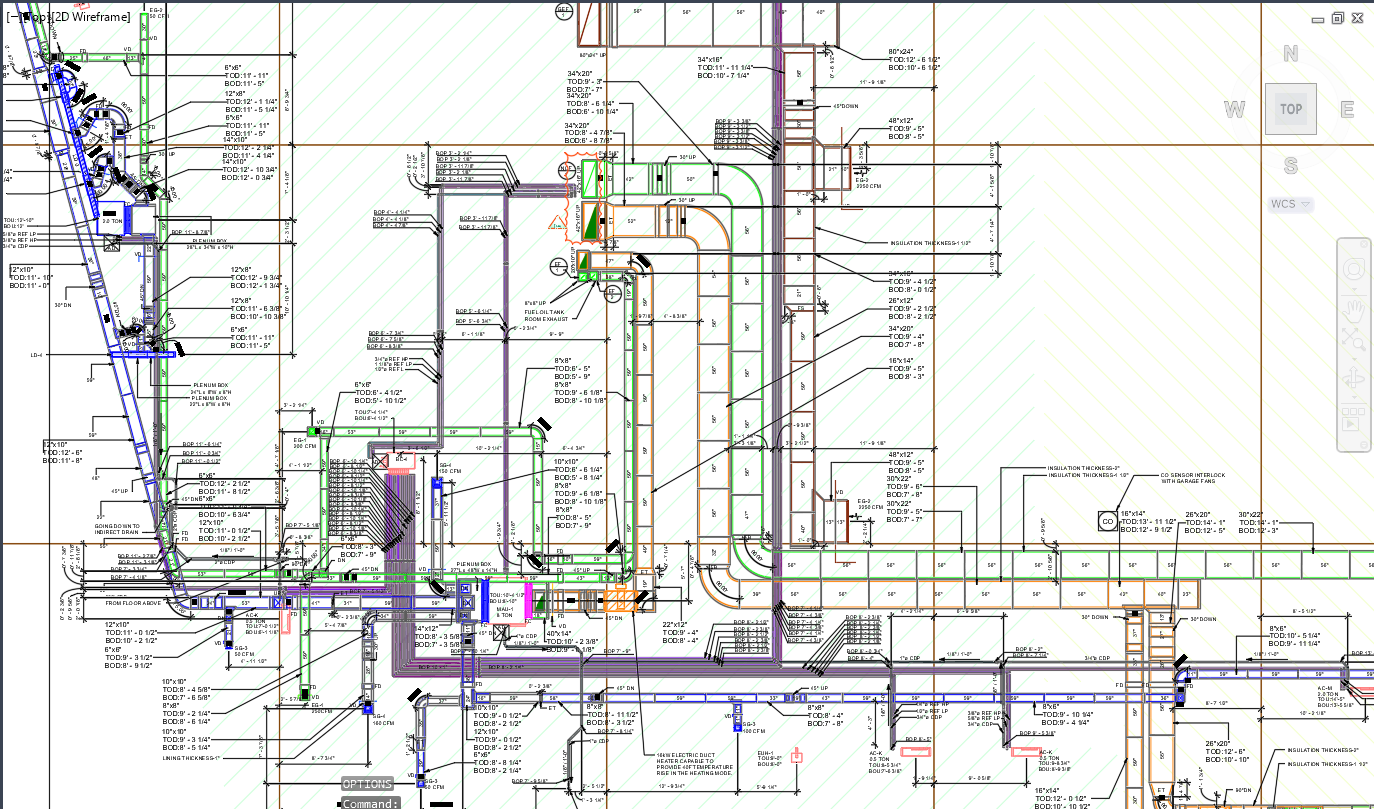
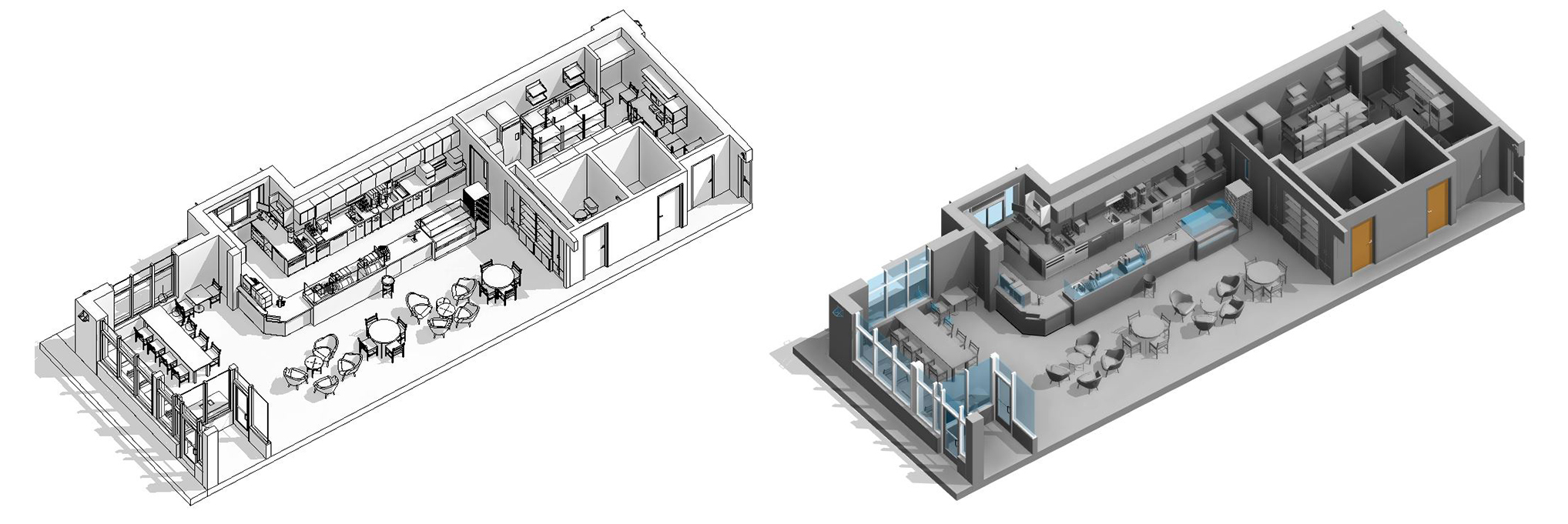
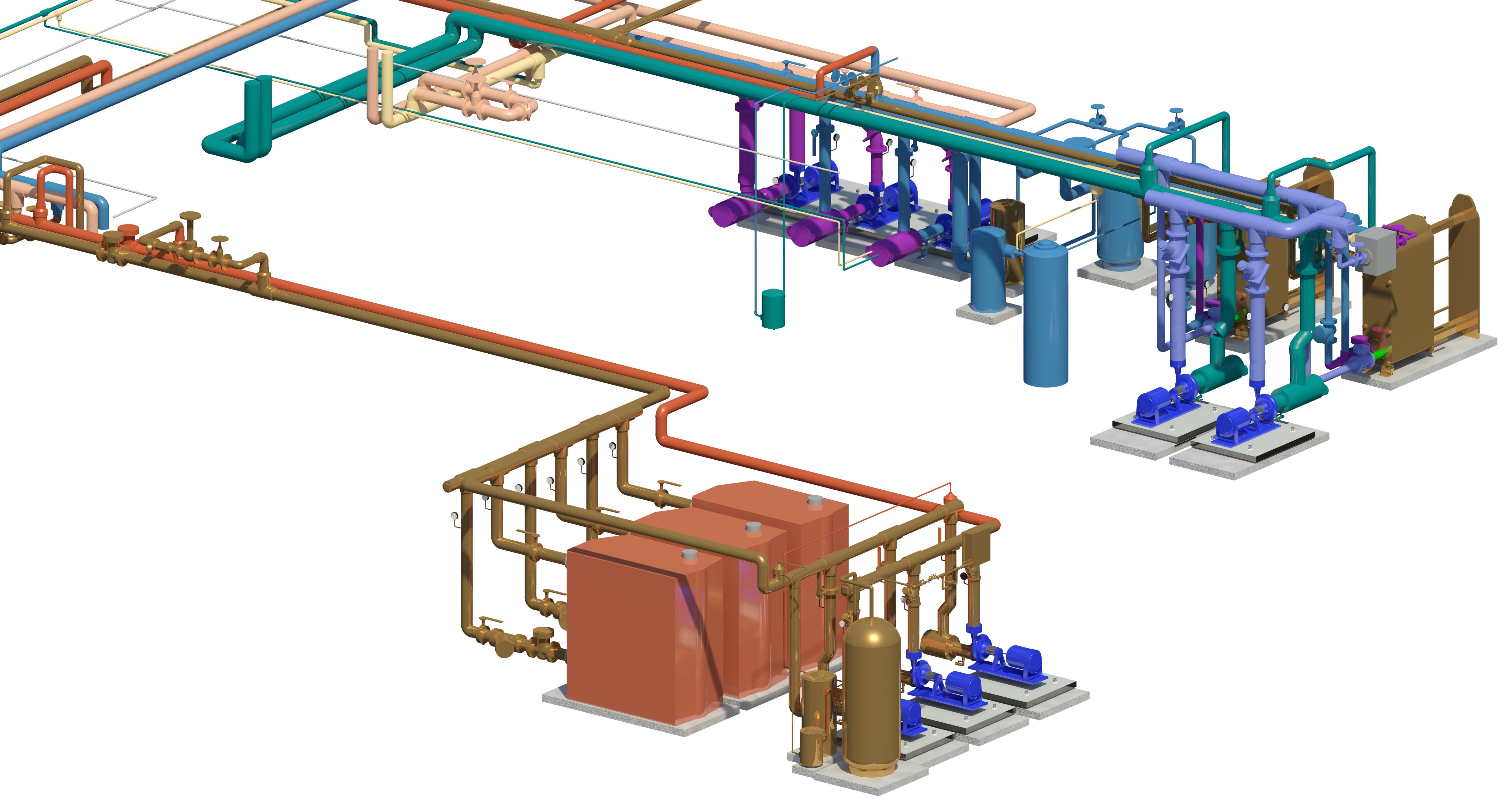
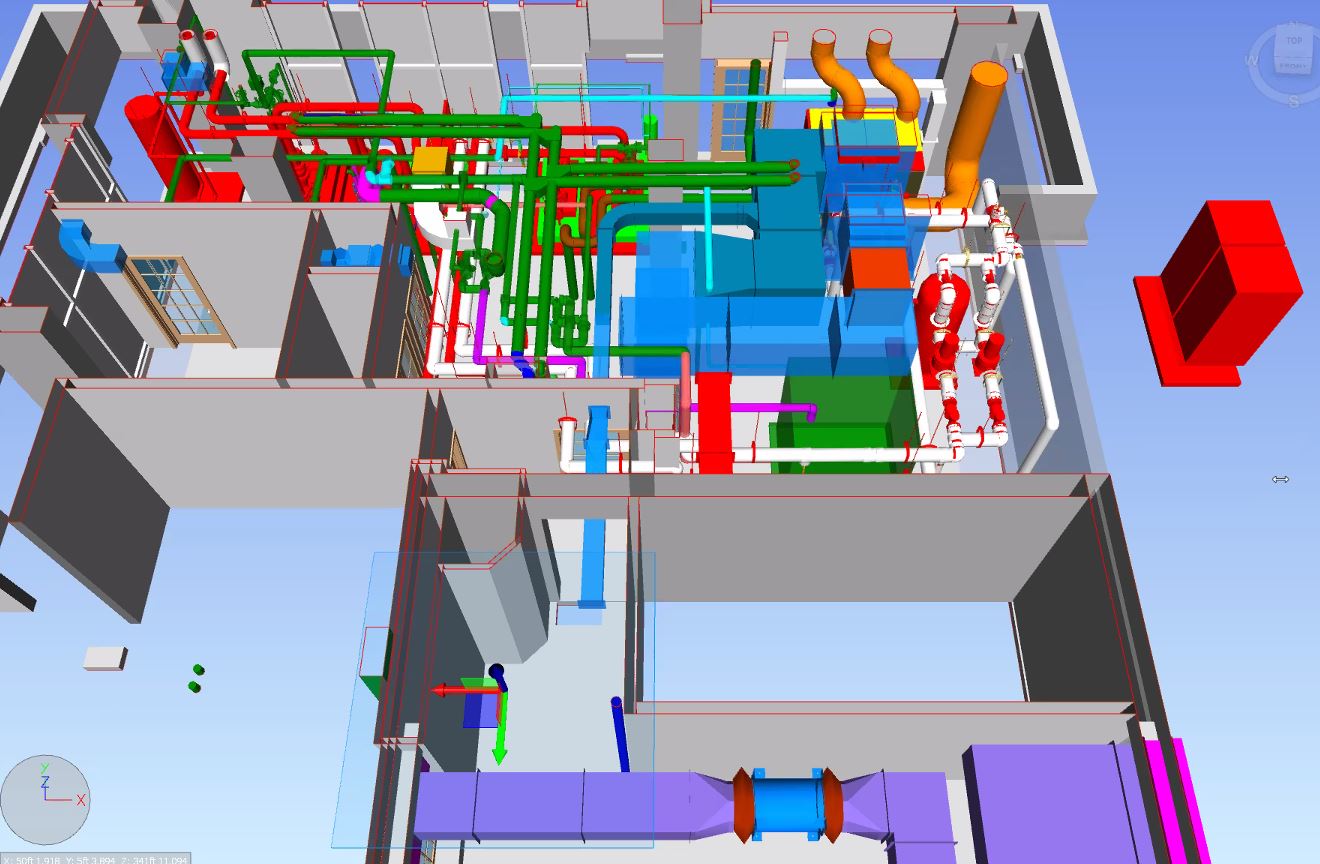
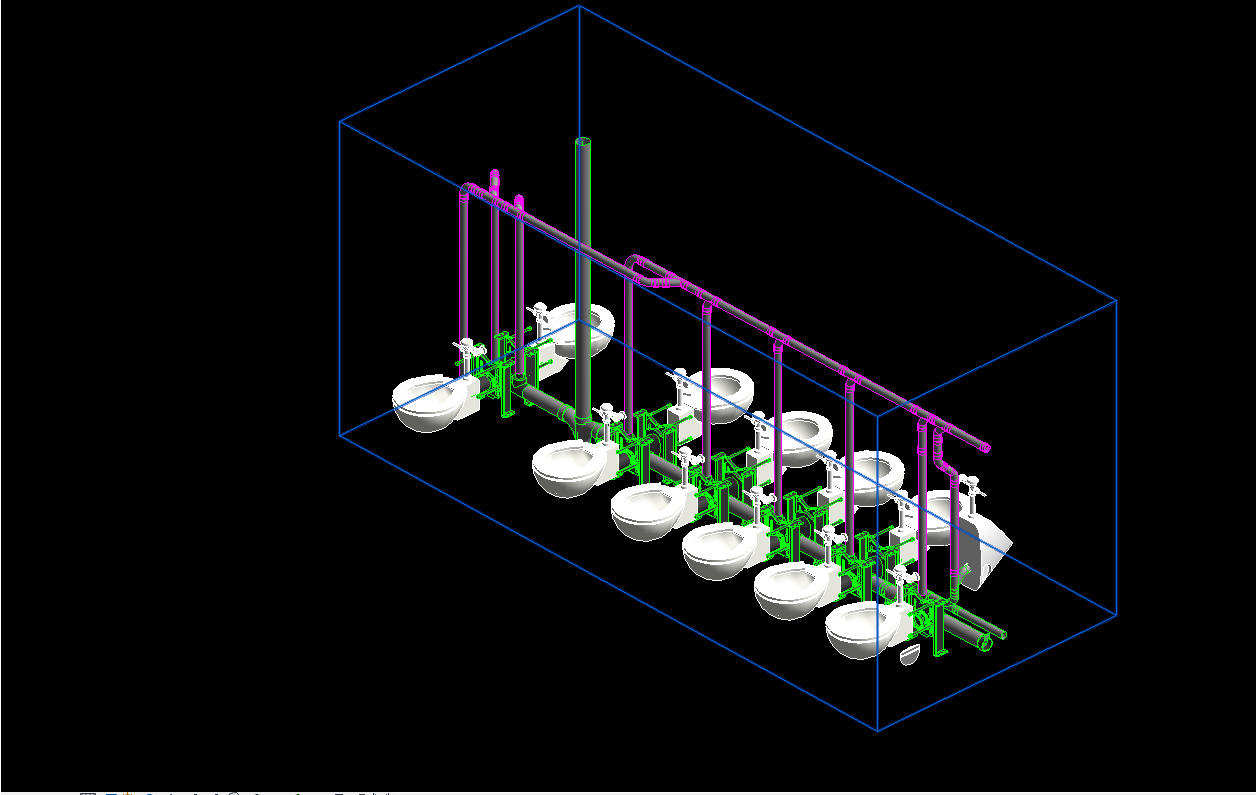
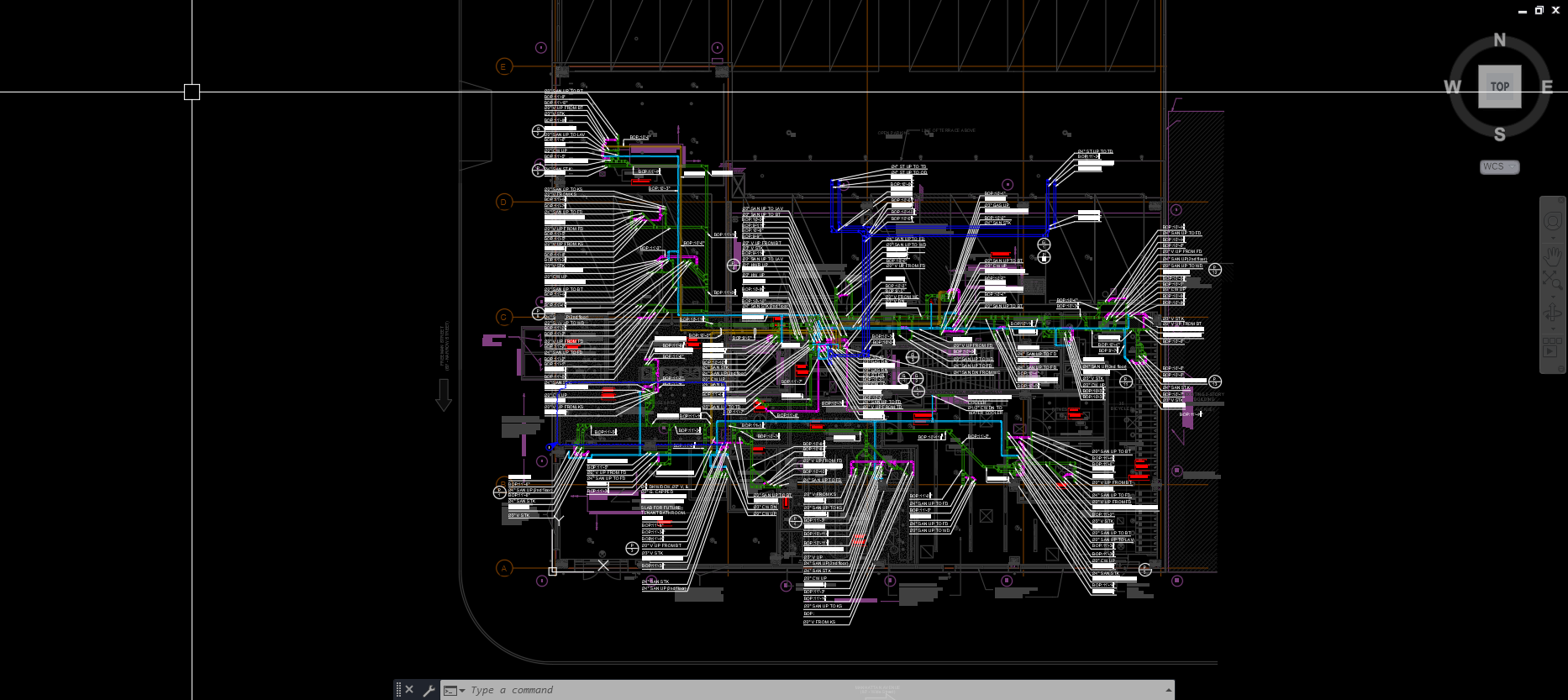
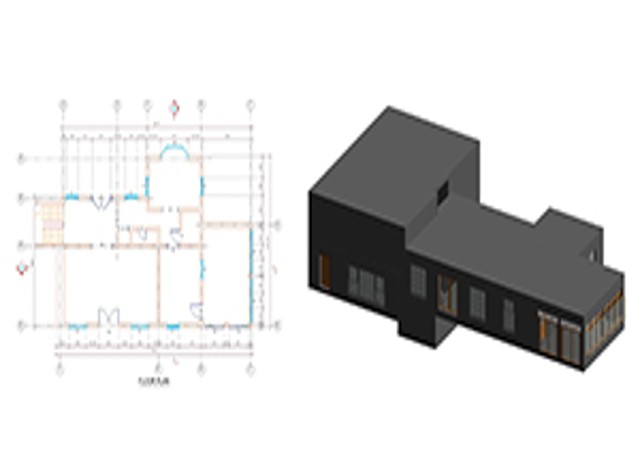
With the adoption of new technologies, advances in digital design tools, inter-connectedness and computer-controlled fabrications are converging to transform every phase of the design and build process. The construction industry is changing. The days of contractors operating in silos are slowly disappearing and being replaced by a system of collaboration and communication, spearheaded by Building Information Modeling, or BIM. BIM is a process, not an application. It’s based around models used for the planning, design, construction and management of building and infrastructure projects faster, more economically and with less environmental impact. It is a process involving the generation and management of digital representations of physical and functional characteristics of places. Building information modelling (BIM) is permeating the AEC industry at an escalating rate to the point where corporations and even countries are choosing to mandate the platform for large-scale projects. BIM models are different from CAD drawings that may be 2D or even 3D. BIM models are made up of intelligent objects that when changed stay updated throughout the design no matter who is working with it.
Why BIM?
Construction woes take a backseat with Building Information Modeling. It allows the more intelligent use of resources, optimization of workflows and leads to productivity and profitability. It allows all interested parties to assess the same information at the same time through the interoperability between different technological platforms. It leads to better outcomes through more effective communication and collaboration.
Be it project management, land surveying, road design, structure design or construction- the role of Building Information Modeling has almost become indispensable for beyond the ordinary results. Using BIM, owners can improve building quality, significantly reduce building lifecycle costs, better understand design projects from beginning to end, optimize operational efficiencies and increase occupancy and use rates.
In construction, Building Information Modeling could be used to monitor the productivity of a construction process. BIM brings the opportunity to try out solutions in advance before building the structure on site: with a constructible model, the structure can be prototyped virtually. Project parties can understand and review the design more easily, which helps guarantee its accuracy and completeness and visualize and evaluate alternatives in terms of cost and other project parameters. BIM leads to better communication between project parties and better quality.
Key Features of BIM:
Uses 3D models to capture, explore, and maintain consistent and coordinated planning, design, construction, and operational data
Provides greater project insight for cost, schedule, and constructability
Uses and shares consistent data whether you’re at your desk or in the field
Enables prompt response to change with processes that are smarter and faster
The preferred software tools used on the BIM platform are Revit Architecture, Revit MEP, Revit Structure, as well as Navisworks, 3D Studio Max and AutoCAD. In addition to buildings, BIM software is used for designing many types of infrastructure, utilities and systems including:
Civil and structural engineering
Energy and utilities
Highway and road engineering
Surveying
Offshore and marine architecture
Rail and metro transportation engineering
Tunnelling and subway architecture
Urban master-planning and smart city design